Radon is a cancer-causing, radioactive gas.
You can’t see radon and you can’t smell it or taste it. But it may be a problem in your home.
Radon is estimated to cause many thousands of deaths each year. That’s because when you breathe air containing radon for extended periods of time, you could potentially develop lung cancer. In fact, the Surgeon General has warned that radon is the second leading cause of lung cancer in the United States. Only smoking causes more lung cancer deaths. If you smoke and your home has high radon levels, your risk of lung cancer is especially high.
Radon comes from the natural (radioactive) breakdown of uranium in soil, rock and water and gets into the air you breathe. It can get into any type of building – homes, offices, and schools and results in a high indoor radon level. But you and your family are most likely to get your greatest exposure at home, where you spend most of your time. Testing is the only way to know if you and your family are at risk from radon. EPA and the Surgeon General recommend testing all homes for radon.
The EPA Recommends:
- Test your home for radon – it’s easy and inexpensive.
- Fix your home if your radon level is 4 picoCuries per liter (pCi/L) or higher.
- Radon levels less than 4 pCi/L still pose a risk, and in many cases may be reduced.
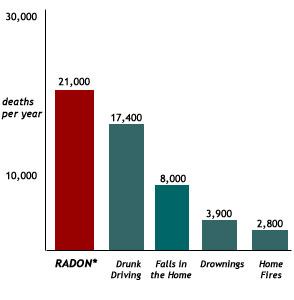
Radon is estimated to cause thousands of lung cancer deaths in the U.S. each year.*
* Radon is estimated to cause about 21,000 lung cancer deaths per year, according to EPA’s 2003 Assessment of Risks from Radon in Homes (EPA 402-R-03-003). The numbers of deaths from other causes are taken from the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention’s 1999-2001 National Center for Injury Prevention and Control Report and 2002 National Safety Council Reports.
Radon Gas Exposure Risk
Radon Risk If You Smoke
| Radon Level | If 1,000 people who smoked were exposed to this level over a lifetime* |
The risk of cancer from radon exposure compares to** | WHAT TO DO: Stop smoking and |
| 20 pCi/L | About 260 people could get lung cancer | 250 times the risk of drowning | Fix your home |
| 10 pCi/L | About 150 people could get lung cancer | 200 times the risk of dying in a home fire | Fix your home |
| 8 pCi/L | About 120 people could get lung cancer | 30 times the risk of dying in a fall | Fix your home |
| 4 pCi/L | About 62 people could get lung cancer | 5 times the risk of dying in a car crash | Fix your home |
| 2 pCi/L | About 32 people could get lung cancer | 6 times the risk of dying from poison | Consider fixing between 2 and 4 pCi/L |
| 1.3 pCi/L | About 20 people could get lung cancer | (Average indoor radon level) | (Reducing radon evels below 2 pCi/L is difficult.) |
| 0.4 pCi/L | About 3 people could get lung cancer | (Average outdoor radon level) | |
| Note: If you are a former smoker, your risk may be lower. * Lifetime risk of lung cancer deaths from EPA Assessment of Risks from Radon in Homes (EPA 402-R-03-003). ** Comparison data calculated using the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention’s 1999-2001 National Center for Injury Prevention and Control Reports. |
|||
Radon Risk If You’ve Never Smoked
| Radon Level | If 1,000 people who never smoked were exposed to this level over a lifetime* | The risk of cancer from radon exposure compares to** | WHAT TO DO: |
| 20 pCi/L | About 36 people could get lung cancer | 35 times the risk of drowning | Fix your home |
| 10 pCi/L | About 18 people could get lung cancer | 20 times the risk of dying in a home fire | Fix your home |
| 8 pCi/L | About 15 people could get lung cancer | 4 times the risk of dying in a fall | Fix your home |
| 4 pCi/L | About 7 people could get lung cancer | The risk of dying in a car crash | Fix your home |
| 2 pCi/L | About 4 person could get lung cancer | The risk of dying from poison | Consider fixing between 2 and 4 pCi/L |
| 1.3 pCi/L | About 2 people could get lung cancer | (Average indoor radon level) | (Reducing radon levels below 2 pCi/L is difficult.) |
| 0.4 pCi/L | (Average outdoor radon level) | ||
| Note: If you are a former smoker, your risk may be higher. * Lifetime risk of lung cancer deaths from EPA Assessment of Risks from Radon in Homes (EPA 402-R-03-003). ** Comparison data calculated using the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention’s 1999-2001 National Center for Injury Prevention and Control Reports. |
|||
Radon concentrations can be fixed!
Radon reduction systems work and they are not too costly. Some radon reduction systems can reduce radon levels in your home by up to 99%. Even very high levels can be reduced to acceptable levels.
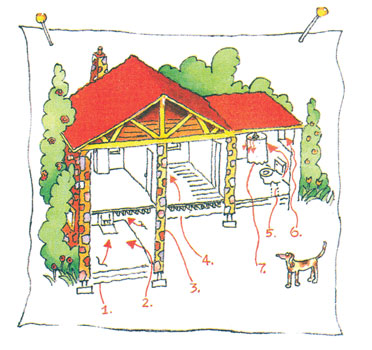
How Does Radon Get Into Your Home?
Radon is a radioactive gas. It comes from the natural decay of uranium that is found in nearly all soils. It typically moves up through the ground to the air above and into your home through cracks and other holes in the foundation. Your home traps radon inside, where it can build up. Any home may have a radon problem. This means new and old homes, well-sealed and drafty homes, and homes with or without basements.
RADON GETS IN THROUGH:
- Cracks in solid floors
- Construction joints
- Cracks in walls
- Gaps in suspended floors
- Gaps around service pipes
- Cavities inside walls
1 out of every 5 homes in the U.S. is estimated to have elevated radon levels. Radon can be found all over the U.S. but portions of Kansas and Missouri are both identified, by the EPA, as being in Zone #1, the highest radon potential in the nation.
The only way to know if your home has elevated radon gas concentrations is to test.